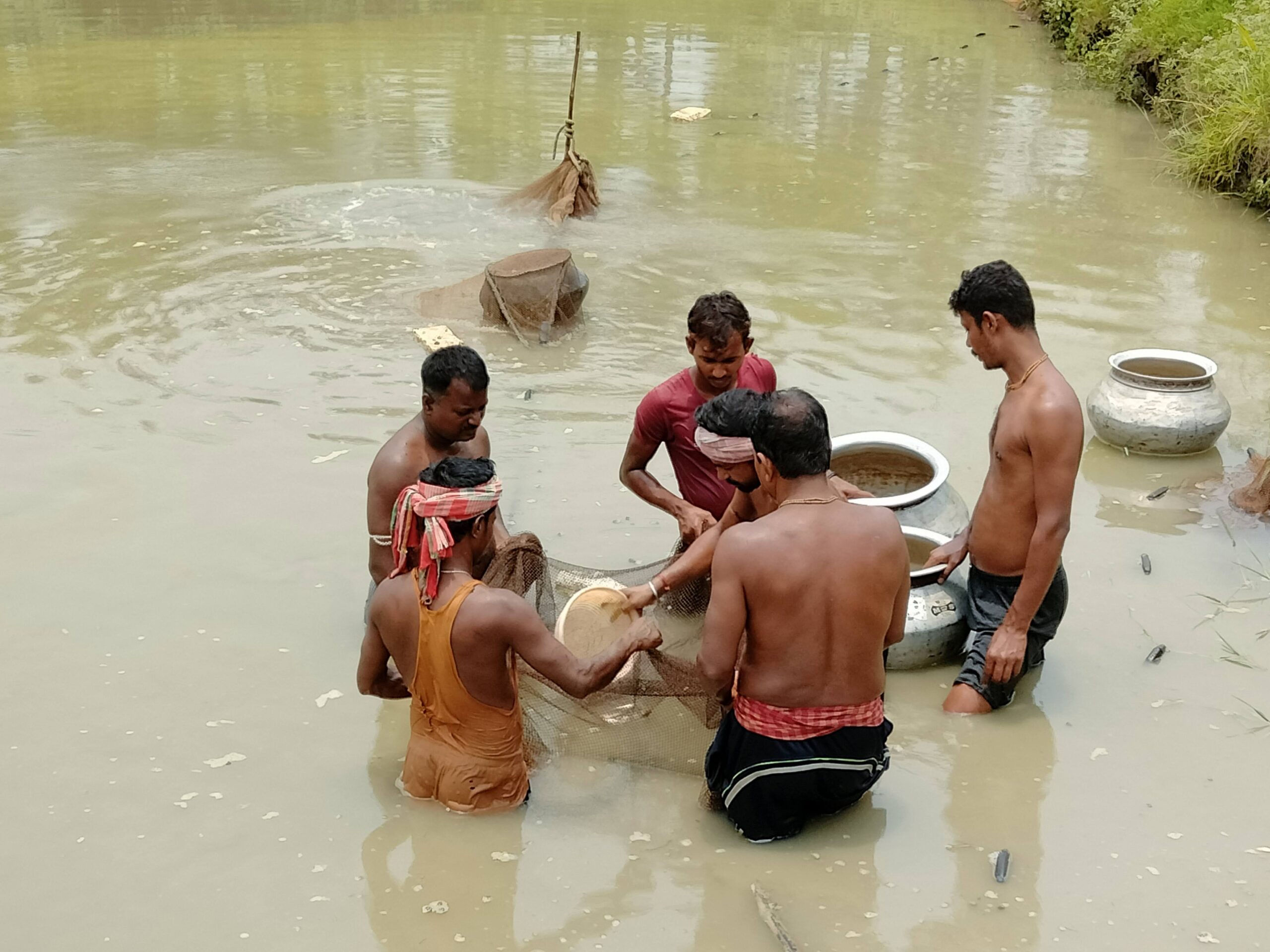
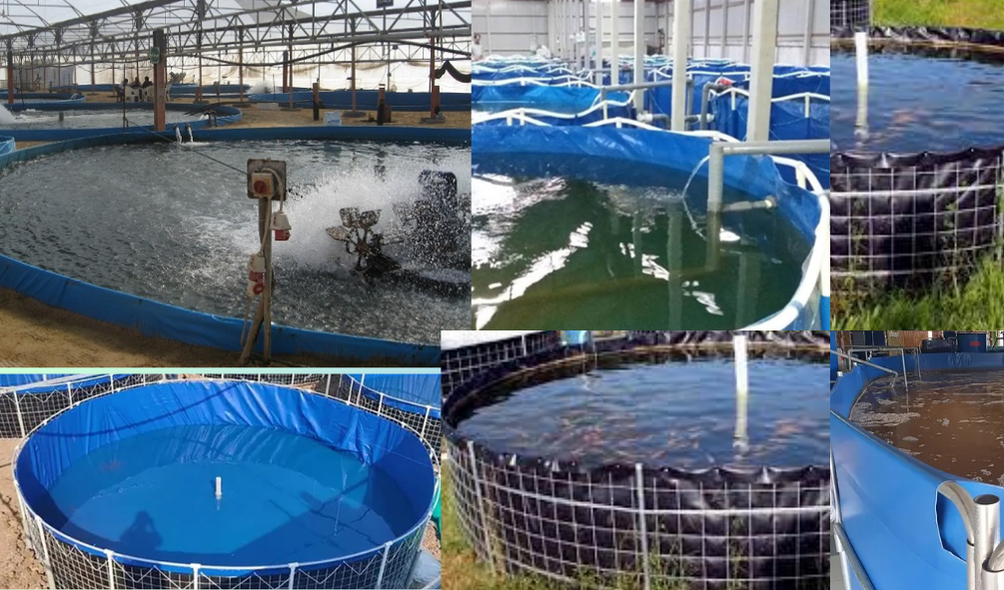
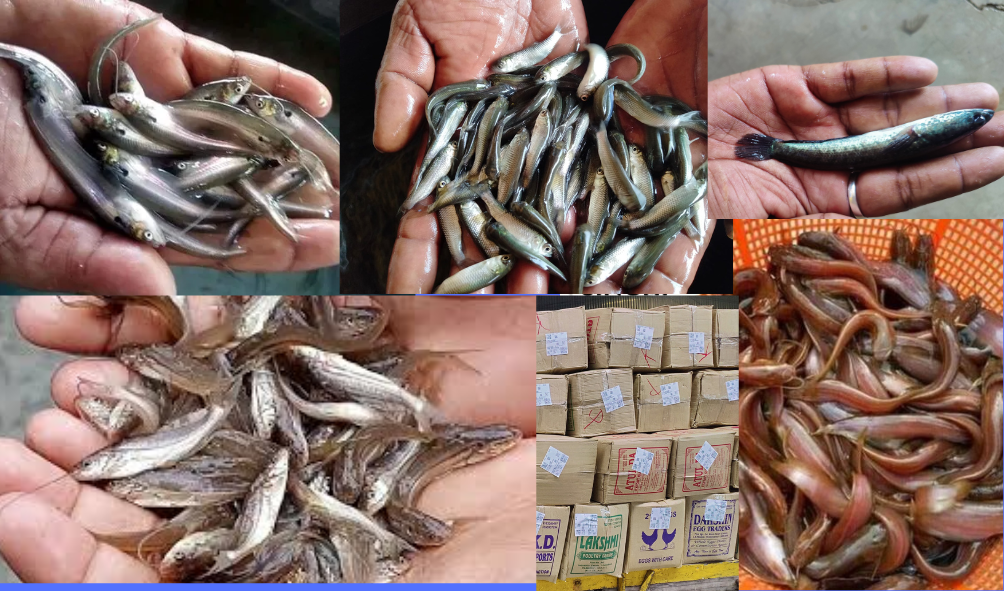
Biofloc fish farming is a sustainable aquaculture technique that enhances water quality and provides a natural food source for fish through the growth of beneficial microbial communities. Here is a basic formula to get started with biofloc fish farming:
Basic Components: Tank or Pond Setup: Size: Depends on the scale, but typically ranges from small tanks (1,000 liters) to large ponds (1,000 cubic meters or more). Material: HDPE-lined ponds, concrete tanks, or plastic tanks. Water: Source: Freshwater (ensure it is free of harmful chemicals and pollutants). Volume: Enough to fill the tank/pond to the desired level. Aeration: Equipment: Air blowers, diffusers, or paddle wheel aerators. Purpose: To provide oxygen and keep the biofloc in suspension. Carbon Source: Common Choices: Molasses, rice bran, wheat bran, or other organic carbon sources. Dosage: Typically 20-30% of the feed's protein content in weight. Microbial Inoculants (optional but beneficial): Types: Probiotics like Bacillus spp., Lactobacillus spp., etc. Purpose: To boost beneficial bacteria growth. Fish Feed: Type: Pelleted commercial feed suitable for the specific fish species. Protein Content: Usually around 25-35%, depending on the species.
Steps to Implement Biofloc System: Preparation: Fill the tank/pond with water and install the aeration system. Check and adjust the water parameters (pH, temperature, salinity if applicable). Inoculation: Add a carbon source to the water (e.g., molasses) to start the microbial activity. Optionally, add microbial inoculants to speed up the process. Monitoring and Adjustment: Regularly monitor water quality parameters (e.g., ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, dissolved oxygen). Maintain a C ratio (carbon to nitrogen) of about 10-15:1 by adjusting the carbon source as needed. Ensure constant aeration to keep the biofloc in suspension and provide sufficient oxygen. Stocking Fish: Once the biofloc has developed (usually 7-10 days), stock the fish into the tank/pond. Common species: Tilapia, shrimp, catfish, and carp are popular choices for biofloc systems. Feeding: Feed the fish with high-quality commercial feed. Adjust feeding rates based on fish growth and biofloc density. Maintenance: Regularly monitor and manage water quality. Harvest fish as they reach market size. Periodically remove excess biofloc if it becomes too dense.
Key Points to Remember: Water Quality: Constantly monitor and maintain optimal water parameters. Aeration: Ensure adequate and continuous aeration. Biofloc Management: Manage the biofloc density to prevent excessive buildup and maintain water quality. Feed Management: Balance feed input to minimize waste and optimize growth. By following these steps and maintaining proper management practices, biofloc fish farming can be an efficient and sustainable method for aquaculture.
FISHMATE LSP
Fishmate LSP will communicate with farmers at the respective area and install biofloc system. Fishmate HO and Fishmate LSP will be guiding farmers upto the production.
Project Information
Client:
Anand Krishi Khamar
Location:
Barrackpore, Kolkata 700122
Website:
https://www.fishmate.in
Inspired Performance
Our Vision to Grow Better
Duty obligations of business it will frequently occur that pleasures have to be repudiated and annoyances accepted.
Read More
Inspired Performance
Our Vision to Grow Better
Duty obligations of business it will frequently occur that pleasures have to be repudiated and annoyances accepted.
Read More
Inspired Performance
Our Vision to Grow Better
Duty obligations of business it will frequently occur that pleasures have to be repudiated and annoyances accepted.
Read More

Subhash Colony, N C Pukur, Barrackpore, Kolkata 700122